This website uses cookies to provide services in accordance with the Privacy Policy. You can specify the conditions for storage or access to cookies in your browser.





Machine learning is a subgroup of the wider field of artificial intelligence. The field of machine learning is devoted to understanding and building a system that can “learn”. It means that system improves performance on some set of tasks based on some data.
In traditional machine learning, learning is divided into 3 main groups due to the nature of the signal or feedback, these are [1]:
In supervised learning an algorithm is trying to find optimal function g:X→Y that maps input data to output data.
Let 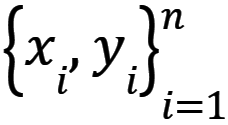 be supervised dataset of n samples such that xi is input (feature vector of i-th sample) and yi is output (class).
be supervised dataset of n samples such that xi is input (feature vector of i-th sample) and yi is output (class).
During learning process input data is feed to Learning system and the Learning system generates output 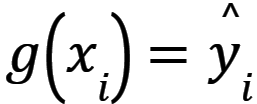 . The optimal function g is selected on the basis of minimalizing summary loss function for all elements of dataset, so that R(g) is minimal, where R(g) is defined by equation (1) [2, 3].
. The optimal function g is selected on the basis of minimalizing summary loss function for all elements of dataset, so that R(g) is minimal, where R(g) is defined by equation (1) [2, 3].
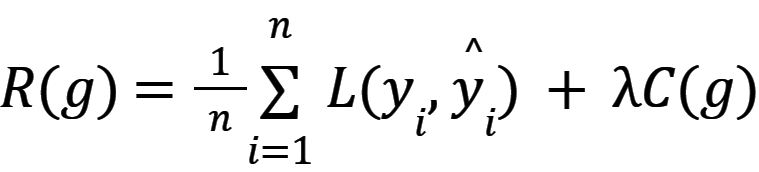
where:
λ – parameter that controls the bias-variance tradeoff.
C(g) - regularization penalty function of g.
In unsupervised learning input data x is not labeled, that means. z=x ϵ Rd, so the algorithm learns patterns within the input data. Method of unsupervised learning can be divided into 3 groups according to task [4]:
Reinforcement learning algorithms learns agents so they can find the way to make a set of actions in an environment that maximize the notion of cumulative reward. Actions for single agents are called policy map – equation 2 and 3 [5].
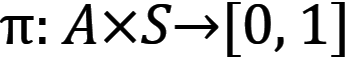
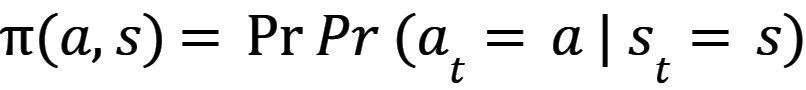
where:
a - action;
s - state.
Function a,s retruns probability of taking action a at state s. The algorithm has to find a policy that maximized expected return – state-value function V(s) which is defined by equation (4) [5].
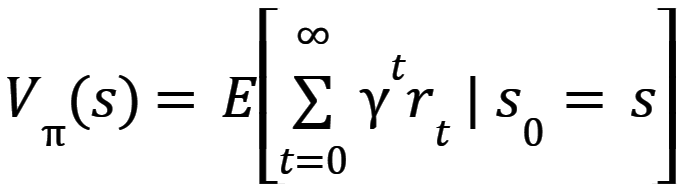
where:
t – timestep;
rt – reward;
γ ϵ [0,1) – discount-rate.
Bibliography:
[1]
H. D. Wehle, „Machine Learning, Deep Learning, and AI: What’s the Difference?”, w Data Scientist Innovation Day, 2017.
[2]
Q. Liu I Y. Wu, „Supervised Learning,” w Encyclopedia of the Sciences of Learning, Boston, MA, Springer, 2012, s. 3243-3245.
[3]
V. Vapnik, „Principles of Risk Minimization for Learning Theory”, w Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, The MIT Press, 1991, s. 831-838.
[4]
IBM, „What is Unsupervised Learning?”, IBM Cloud Education, 21 09 2020. [Online]. Available: https://www.ibm.com/cloud/learn/unsupervised-learning. [Date of access: 14 07 2022].
[5]
R. S. Sutton i A. G. Barto, Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction, MIT Press, 2018.
